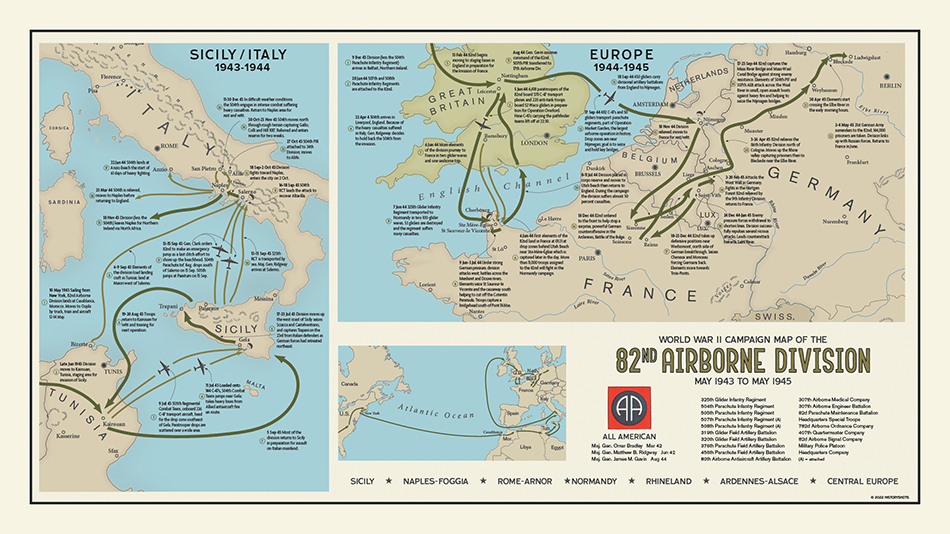
82nd Airborne Division - All american Division
Activated 25 Mar 1942 • Entered Combat 9 Jul 1943 at Sicily • Days of Combat 422 • Casualties 9,073
Commanding Generals
Maj. Gen. Omar Bradley Mar 42
Maj. Gen. Matthew B. Ridgway Jun 42
Maj. Gen. James M. Gavin Aug 44
Campaigns
Sicily (9 Jul - 17 Aug 43)
Naples-Foggia (9 Sep 43 - 21 Jan 44)
Rome-Arno (22 Jan 44 - 9 Sep 44)
Normandy (6 Jun 44 - 24 Jul 44)
Rhineland (15 Sep 44 - 21 Mar 45)
Ardennes-Alsace (16 Dec 44 - 25 Jan 45)
Central Europe (22 Mar 45 - 11 May 45)
This campaign map shows the route of the 82nd Airborne Division during World War II. This chart is available for purchase at HistoryShots.com.
Division Chronicle
The 82d Airborne Division landed at Casablanca, 10 May 1943, and trained. Elements first saw combat in Sicily, when the 505th RCT and part of the 504th dropped behind enemy lines, 9-10 July 1943, at Gela. The remainder of the 504th RCT dropped, 11-12 July 1943, also near Gela, after running friendly naval and ground force fire. Scattered elements formed and fought as ground troops.
The elements were flown back to Tunisia for reequipment and returned to Sicily to take off for drop landings on the Salerno beachhead. The 504th Parachute Infantry dropped, 13 September 1943, and the 505th the following night; the 325th landed by boat. These elements bolstered Salerno defenses and fought their way into Naples, 1 October 1943.
After a period of occupation duty (and combat for some elements in the Volturno Valley and Anzio beachhead), the Division moved to Ireland, November 1943, and later to England, February 1944, for additional training.
Moving in by glider and parachute, troops of the 82d dropped behind enemy lines in Normandy on D-day, 6 June 1944, before ground troops hit the beaches. Cutting off enemy reinforcements, the Division fought its way from Carentan to St. Sauveur-le-Vicomte, fighting 33 days without relief. Relieved on 8 July, it returned to England for refitting. On 17 September, it was dropped at Nijmegen, 50 miles behind enemy lines, and captured the Nijmegen bridge, 20 September, permitting relief of British paratroops by the British 2d Army. After heavy fighting in Holland, the Division was relieved 11 November and rested in France. It was returned to combat, 18 December 1944, to stem the von Rundstedt offensive, blunting the northern salient of the Bulge. It punched through the Siegfried Line in early February 1945, and crossed the Roer, 17 February. Training with new equipment in March, the Division returned to combat, 4 April, patrolling along the Rhine, securing the Koln area, later moving across the Elbe, 30 April, into the Mecklenburg Plain, where, 2 May 1945, the German 21st Army surrendered.
Division Organization
325th Glider Infantry Regiment
504th Parachute Infantry Regiment
505th Parachute Infantry Regiment
507th Parachute Infantry Regiment (A)
508th Parachute Infantry Regiment (A)
HHB Division Artillery
319th Glider Field Artillery Battalion
320th Glider Field Artillery Battalion
376th Parachute Field Artillery Battalion
456th Parachute Field Artillery Battalion
80th Airborne Antiaircraft Artillery Battalion
307th Airborne Medical Company
307th Airborne Engineer Battalion
82d Parachute Maintenance Battalion
Headquarters Special Troops
782d Airborne Ordnance Company
407th Quartermaster Company
82d Airborne Signal Company
Military Police Platoon
Headquarters Company
A = attached
Date Activated is the date the division was activated or inducted into federal service (national guard units).
Casualties are number of killed, wounded in action, captured, and missing.
The dates after the campaign name are the dates of the campaign not of the division.
The Army Almanac: A Book of Facts Concerning the Army of the United States; , U.S. Government Printing Office. Army Battle Casualties and Nonbattle Deaths in World War II, Final Report, 1 December 1941 - 31 December 1946. US Army Center of Military History at http://www.history.army.mil/ Various divisional histories